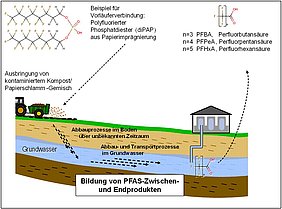
In the project, a trace-analytical method was developed for short-chain, mobile per- and polyfluorinated substances (PFASs), with which a significant point source of trifluoroacetate (TFAA) could be identified in the Neckar river. A method to remove short-chain PFASs using ion exchangers was also developed.
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) are anthropogenic substances with a broad application in industry and in households. Various long-chain representatives of this group include the PBT chemicals (persistent, bioaccumulative, toxic), and their use has been restricted in some cases (EU Directive 2006/122/EC: Ban on perfluorooctane sulfonic acid (PFOS)). They are now frequently replaced by short-chain PFASs with four to six fluorinated carbon atoms. The release of fire-fighting foams during fire-fighting and fire-fighting trainings as well as the incorrect disposal of paper-fibre biosolids are significant contamination sources of PFASs in groundwater and surface water, and have already caused the decommissioning of waterworks.
The digestion method pursued in the project for precursors of perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acids via hydrolysis or mild oxidation could not be achieved due to incomplete conversion or the generation of volatile and difficult-to-analyse products. However, it was possible to develop a method of analysis for short-chain perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acids with which a significant point source for trifluoroacetate (TFAA) could be identified in the Neckar river.
It was shown that short-chain PFASs can be removed using weak anion exchangers from raw water. However, the cost effective operation requires the addition of an organic solvent (ethanol) to regenerate the absorber, which limits the practical application of the method.
Publications:
Lange, F. T.; Riegel, M.; Janda, J.; Brauch, H.-J.: Analytik kurzkettiger PFAS und deren technische Entfernung durch Ionenaustausch [Analysis of short-chain PFAS and their technical removal using ion exchange]. DVGW energie|wasser-praxis 05/2018, 64-71 (2018)
Janda, J.; Nödler, K.; Brauch, H.-J.; Zwiener, C.; Lange, F. T.: Robust trace analysis of polar (C2-C8) perfluorinated carboxylic acids by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry: method development and application to surface water, groundwater and drinking water. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. 26(8), 7326-7336 (2018)


![[Translate to English:] Prüfstelle-Produktprüfung_Teststand Test centre and product testing](/fileadmin/_processed_/0/9/csm_TZW-Karlsruhe_Pruefung_Geraete-Teststand_444204ae51.jpg)